The evolution of talent acquisition from a mere task of filling vacancies to a strategic imperative shaping organizational success has been remarkable. Today, talent acquisition stands as a pivotal partner, driving growth, innovation, and competitiveness within companies.
However, achieving this level of strategic alignment requires a structured approach, starting with understanding your organization’s talent maturity level—essentially, the sophistication of your recruitment processes.
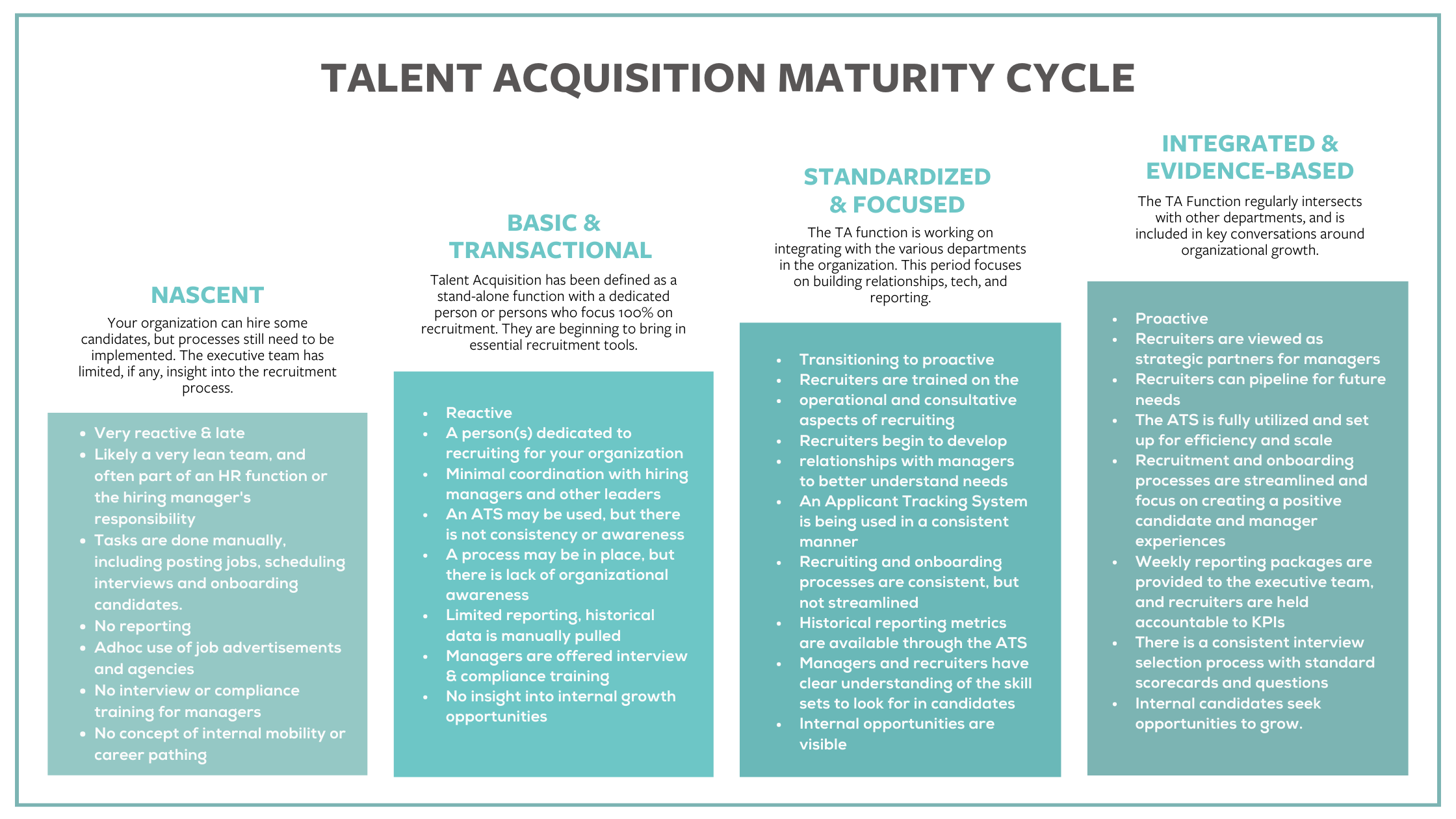
The Talent Acquisition Maturity Cycle serves as a guide to help organizations assess their current efforts and progress through distinct phases of maturity. Each phase signifies a leap forward, transitioning from rudimentary and reactive practices to strategic methodologies that fuel organizational success.
In this blog, we’ll delve into the distinctive characteristics of each phase of the Talent Acquisition Maturity Model, empowering organizations to pinpoint their current position and determine the optimal next steps for advancement.
- Nascent
- Basic & Transactional
- Standardized & Focused
- Integrated & Evidence Based
Phase 1: Nascent
In phase one, recruitment processes are in their infancy. While organizations in this phase can hire candidates, the lack of processes and strategic involvement is evident.
Key Characteristics:
Limited Insight and Very Reactive
Decisions are often reactive, driven by immediate needs rather than strategic foresight. This can lead to delayed responses to hiring needs and challenges in maintaining a competitive edge in acquiring top talent.
Lean Structure and Manual Processes
Recruitment tasks fall under HR or hiring managers who manually execute job postings, interviews, and onboarding. While this may suffice for basic recruitment needs, it lacks the efficiency and scalability required for sustained success
Ad Hoc Practices and Limited Reporting
Recruitment efforts rely on sporadic job advertisements and external agencies. There is a lack of cohesive strategy and reporting, hindering the ability to track key performance indicators (KPIs), and make data-driven decisions.
Training Gaps & Internal Mobility
Managers may lack interview or compliance training, impacting candidate quality and evaluation consistency. Internal mobility opportunities and career pathing are overlooked, limiting ability to retain and develop existing talent.
Phase 2: Basic & Transactional
As organizations transition into this phase, talent acquisition has been established as a stand-alone function with a dedicated person or team that focuses on recruitment.
Key Characteristics:
Emergence of Essential Tools
Basic recruitment tools are introduced such as an Applicant Tracking System (ATS), marking a shift towards greater efficiency and organization in managing candidate workflows.
Minimal Coordination and Awareness
Coordination with hiring managers and other leaders is minimal. There may be a lack of awareness across the organization regarding recruitment processes and the role of the recruitment function in supporting strategic business goals.
Introduction of Training Initiatives
Recruiters and hiring managers receive training on processes, interview techniques, and compliance. These training initiatives aim to improve the quality and consistency of candidate evaluations and hiring decisions.
Limited Reporting and Data
While there is a semblance of process, reporting continues to be limited. Recruitment data may be manually pulled from an ATS or other sources, hindering the ability to conduct an in-depth analysis.
Focus on External Recruitment
Recruitment efforts primarily revolve around external candidate acquisition. While internal mobility and career pathing may be acknowledged, they are not yet fully integrated into the strategy.
Phase 3: Standardized & Focused
This phase represents a shift towards integration, consistency, and strategic alignment within the recruitment function. Organizations focus on building relationships, leveraging technology, and enhancing reporting capabilities.
Key Characteristics:
Operational Integration
Talent acquisition aligns with various departments across the organization. Recruiters actively engage with hiring managers and department leaders to understand and align with business needs, talent requirements, and organizational goals.
Tech Adoption and Process Standardization
Recruiters consistently leverage an ATS and other tools to streamline candidate workflows, improve communication, and create efficiencies. Standardizing recruitment processes is a priority to ensure consistency and quality in candidate experiences.
Improved Reporting and Data Analytics
Implemented technology enables organizations to generate detailed reports, track KPIs, and derive actionable insights. This reporting enables leaders to optimize recruitment strategies, identify trends, and address potential bottlenecks.
Strategic Partnerships and Skill Alignment
Recruiters develop strong relationships with hiring managers and align recruitment efforts with skill sets required for organizational success. Recruitment initiatives are targeted, efficient, and closely aligned with business priorities.
Enhanced Candidate and Manager Experiences
Candidates encounter streamlined workflows, clear communication, and positive interactions with recruiters. Hiring managers benefit from standardized processes, timely updates, and access to candidates who effectively match their requirements.
Visibility of Internal Opportunities
Recruiters actively promote internal job postings, facilitate talent mobility initiatives, and support career pathing within the organization. Promoting internal opportunities enhances engagement and retention while fostering a culture of continuous growth.
Phase 4: Integrated & Evidence Based
In this phase, talent acquisition has transformed into a strategic partner that is embedded in the organization’s growth discussions and goals.
Key Characteristics:
Proactive Practices
Recruiters work closely with hiring managers and organizational leaders to anticipate future talent needs, collaborate with leaders on workforce planning, and align strategies with business objectives.
Full Tech Utilization
The ATS and other recruitment tools are being used to their fullest potential to optimize efficiency, scalability, and seamless candidate experiences. Recruiters harness automation and AI-driven analysis to improve recruitment outcomes.
Data-Driven Decision-Making
Leaders receive weekly reports, analyze data, and derive actionable insights to drive informed decision-making. Recruiters are held accountable to KPIs to ensure alignment with organizational goals.
Standardized Processes
Processes are standardized, consistent, and focused on quality assurance. There is a clear interview selection process with standard scorecards, questions, and evaluation criteria to ensure a rigorous yet fair process, leading to optimal hiring decisions.
Focus on Candidate and Manager Experiences
Candidates encounter streamlined workflows, transparent communication, and personalized interactions. Similarly, hiring managers benefit from efficient processes and access to top-tier candidates who align with their team’s needs.
Talent Development and Retention
Organizations facilitate internal mobility programs and support career growth discussions for existing employees. Employees are encouraged to seek internal opportunities, fostering a culture of continuous development and retention.
Regardless of your organization’s current phase, a seasoned RPO partner like Hueman can propel your efforts to the next level. Get in touch with us today to discover how we can help you along your organization’s talent acquisition journey.
Looking for more ways to strengthen your recruitment process? Download the World-Class Recruitment Guide.







